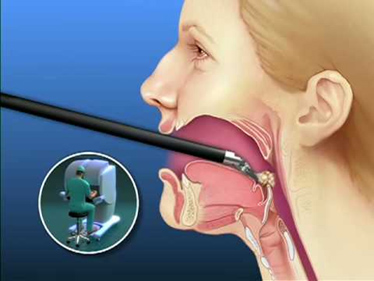
Overview
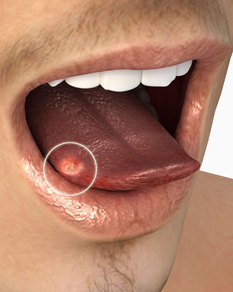
Tongue cancer is a type of mouth cancer, or oral cancer, that usually develops in the squamous cells on the surface of the tongue. It can cause tumors or lesions. The most noticeable signs of tongue cancer are a sore on the tongue that does not heal and a painful tongue.
Cancer can develop in two different areas of the tongue. Tongue cancer develops at the front of the tongue, while cancer at the back of the tongue is known as or opharyngeal cancer.
Symptoms of Tongue Cancer
The most common type of tongue cancer is called squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cells are thin, flat cells that are present on the surface of the skin and the tongue, in the lining of the digestive and respiratory tracts, and in the lining of the mouth, throat, thyroid, and larynx.
The primary symptoms of tongue cancer are a painful tongue and the development of a sore on the tongue. Additional symptoms may include:
- Pain in the jaw or throat
- Pain when swallowing
- Feeling as though something is catching in the throat
- A stiff tongue or jaw
- Problems swallowing or chewing food
- A red or white patch forming on the lining of the mouth or tongue
- A tongue ulcer that will not heal
- Numbness in the mouth
- Bleeding from the tongue without reason
- A lump on the tongue that does not go away
The symptoms of tongue cancer are similar to those of other oral cancers, and they may also not be evident in the early stages of the disease. It is also possible for people to have some of these symptoms without having tongue cancer or another type of oral cancer.