What is Diagnostic Laparoscopy?
The laparoscopy done to diagnose abdominal problems when definitive diagnosis is not done with non invasive procedures like sonography, CT scan etc


The laparoscopy done to diagnose abdominal problems when definitive diagnosis is not done with non invasive procedures like sonography, CT scan etc
The surgery is performed under
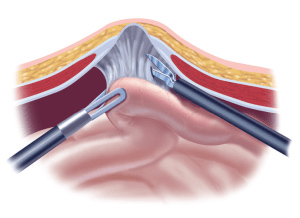
A laparoscope (a tiny telescope) connected to a special camera is inserted through the port. This gives the surgeon a magnified view of the patient’s internal organs on a television screen.
Other ports are inserted which allow your surgeon to see the internal organs and make a decision on the proper diagnosis or treatment.
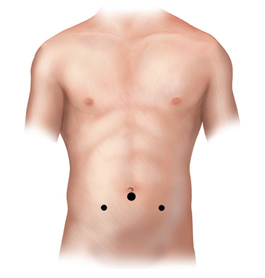
After the surgeon completes the operation, the small incisions are closed with absorbable sutures or with surgical tapes.
General complications of any operation
Specific complications of this operation: rare but possible
Laparoscopy has a role in the diagnosis of both acute and chronic abdominal pain. There are many causes of abdominal pain. Some of these causes include appendicitis, adhesions or intra-abdominal scar tissue, pelvic infections, endometriosis, abdominal bleeding and, less frequently, cancer. It is used in patients with irritable bowel disease to exclude other causes of abdominal pain. Surgeons can often diagnose the cause of the abdominal pain and, during the same procedure, correct the problem.
A patient may have a lump (mass or tumor), which can be felt by the doctor, the patient, or seen on an X-ray. Most masses require a definitive diagnosis before appropriate therapy or treatment can be recommended. Laparoscopy is one of the techniques available to your physician to look directly at the mass and obtain tissue to discover the diagnosis.
The presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity is called ascites. Sometimes the cause of this fluid accumulation cannot be found without looking into the abdominal cavity, which can often be accomplished with laparoscopy.
Non-invasive imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scan (computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) may discover a mass inside or on the surface of the liver. If non-invasive imaging cannot give your physician enough information, a liver biopsy may be needed to establish the diagnosis. Diagnostic laparoscopy is one of the safest and most accurate ways to obtain tissue for diagnosis. In other words, it is an accurate way to collect a biopsy to sample the liver or mass without actually opening the abdomen.
Your doctor may need information regarding the status of a previously treated disease, such as cancer. This may occur after treatment with some forms of chemotherapy or before more chemotherapy is started. Also, information may be provided by diagnostic laparoscopy before planning a formal exploration of the abdomen, chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Some cases it is needed to look and rectify causes of non conception.
There are other reasons to undergo a diagnostic laparoscopy, which cannot all be listed here. This should be reviewed and discussed with your surgeon.