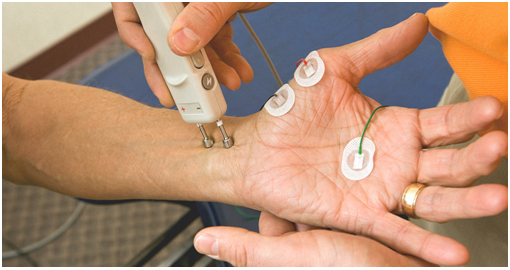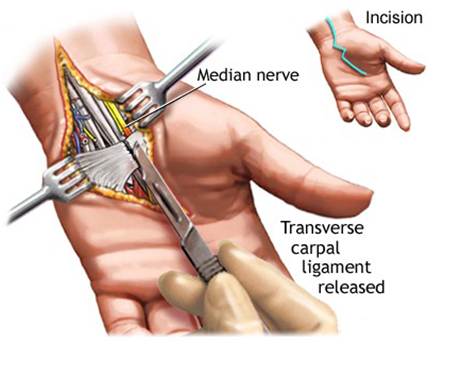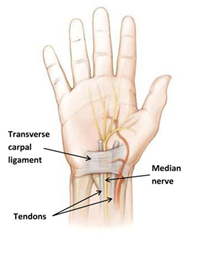
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition that causes pain, numbness, tingling and weakness in the hand and wrist. It occurs when there is increased pressure within the wrist on a nerve called the median nerve. This nerve provides sensation to the thumb, index, and middle fingers, and to half of the ring finger. The small finger (the “pinky”) is typically not affected. The median nerve also provides strength to some of the muscles at the base of the thumb and index finger.
What is the carpal tunnel ?
The carpal tunnel is a narrow canal or channel in the wrist. The bottom and sides of the tunnel are formed by a semi-circle of bones called carpal bones. A strong tissue, called a ligament, forms the top of the tunnel. The median nerve and tendons pass through this narrow space. The tendons are rope-like structures that connect muscles in the forearm to bones in the hand. Tendons allow the fingers and thumb to bend and straighten. Conditions that further narrow the carpal tunnel or cause the tendons that pass through this tunnel to swell cause carpal tunnel syndrome by compressing the median nerve.